6 月 . 16, 2024 12:52 Back to list
Sealed with molded gasket.
Molded Gaskets A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Gaskets are essential components in various industries, providing sealing solutions for pipes, tanks, and other equipment. Molded gaskets, also known as compression gaskets, are one of the most popular types due to their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to molded gaskets, including their types, materials, manufacturing processes, applications, and maintenance.
What Are Molded Gaskets?
Molded gaskets are made by molding a material under heat and pressure to create a flexible, self-sealing ring. This process allows for the creation of complex shapes and designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other gasket types. Molded gaskets can be made from a variety of materials, including rubber, silicone, PTFE, and neoprene, among others.
Types of Molded Gaskets
There are several types of molded gaskets available, each with its own unique properties and applications. Some of the most common types include
1. Rubber Molded Gaskets These gaskets are made from natural or synthetic rubber and are suitable for a wide range of applications, including plumbing, HVAC, and chemical processing.
2. Silicone Molded Gaskets Silicone gaskets are known for their、,、。
3. PTFE Molded Gaskets PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is a highly durable and chemical-resistant material that is commonly used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
4. Neoprene Molded Gaskets Neoprene, or polychloroprene, is a synthetic rubber that is resistant to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it a popular choice for outdoor applications.
Manufacturing Process of Molded Gaskets
The manufacturing process of molded gaskets typically involves the following steps
1. Material Selection The first step is to select the appropriate material based on the specific requirements of the application.
2. Mold Design Next, a mold is designed to match the dimensions and shape of the gasket. The mold is usually made of metal and can be either two-piece or multi-piece.
3. Material Preparation The selected material is then prepared by mixing it with additives and curing agents, if necessary.
4. Molding The prepared material is then poured into the mold and subjected to heat and pressure to cure and form the gasket.
5. Curing After molding, the gasket is allowed to cure at room temperature or under controlled conditions to ensure proper bonding and stability.
6. Demolding Once the gasket has cured, it is removed from the mold and inspected for any defects or inconsistencies.
7
7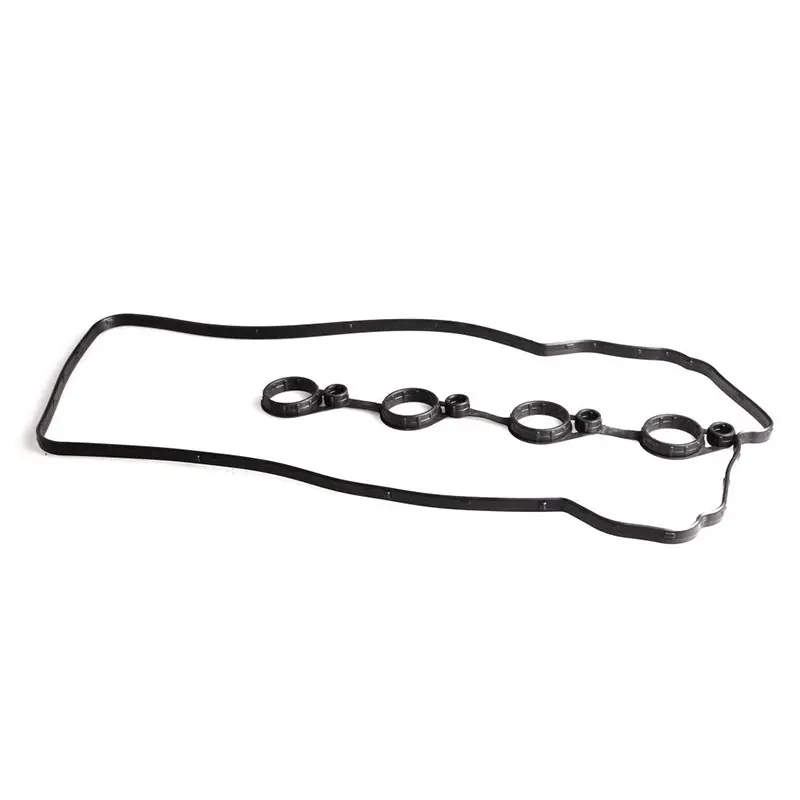 7
7
7
7 molded gasket. Finishing Finally, the gasket may undergo additional finishing processes, such as cutting, trimming, and buffing, to meet specific requirements.
Applications of Molded Gaskets
Molded gaskets are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and performance. Some of the most common applications include
1. Plumbing Systems Molded gaskets are commonly used in plumbing systems to provide a watertight seal between pipes, fittings, and valves.
2. HVAC Systems In HVAC systems, molded gaskets are used to seal ductwork, air handlers, and other components to prevent air leaks and maintain optimal indoor air quality.
3. Chemical Processing Molded gaskets are ideal for use in chemical processing applications due to their resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures.
4. Food Processing In food processing plants, molded gaskets are used to seal equipment and machinery to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity.
5. Automotive Industry Molded gaskets are used in the automotive industry to seal engine blocks, transmission cases, and other components to prevent leaks and ensure proper operation.
Maintenance of Molded Gaskets
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of molded gaskets. Some tips for maintaining molded gaskets include
1. Regular Inspection Regularly inspect molded gaskets for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Replace any damaged or worn gaskets promptly.
2. Cleaning Clean molded gaskets regularly to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can affect their performance. Use mild cleaning solutions and avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the gasket material.
3. Proper Installation Ensure that molded gaskets are installed correctly and tightened to the recommended torque to ensure a proper seal.
4. Storage Store molded gaskets in a dry, clean environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures to prevent damage or degradation.
Conclusion
Molded gaskets are versatile, durable, and cost-effective sealing solutions that are widely used in various industries. By understanding the different types of molded gaskets, their materials, manufacturing processes, applications, and maintenance requirements, you can choose the right gasket for your specific needs and ensure optimal performance and longevity.
molded gasket. Finishing Finally, the gasket may undergo additional finishing processes, such as cutting, trimming, and buffing, to meet specific requirements.
Applications of Molded Gaskets
Molded gaskets are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and performance. Some of the most common applications include
1. Plumbing Systems Molded gaskets are commonly used in plumbing systems to provide a watertight seal between pipes, fittings, and valves.
2. HVAC Systems In HVAC systems, molded gaskets are used to seal ductwork, air handlers, and other components to prevent air leaks and maintain optimal indoor air quality.
3. Chemical Processing Molded gaskets are ideal for use in chemical processing applications due to their resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures.
4. Food Processing In food processing plants, molded gaskets are used to seal equipment and machinery to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity.
5. Automotive Industry Molded gaskets are used in the automotive industry to seal engine blocks, transmission cases, and other components to prevent leaks and ensure proper operation.
Maintenance of Molded Gaskets
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of molded gaskets. Some tips for maintaining molded gaskets include
1. Regular Inspection Regularly inspect molded gaskets for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Replace any damaged or worn gaskets promptly.
2. Cleaning Clean molded gaskets regularly to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can affect their performance. Use mild cleaning solutions and avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the gasket material.
3. Proper Installation Ensure that molded gaskets are installed correctly and tightened to the recommended torque to ensure a proper seal.
4. Storage Store molded gaskets in a dry, clean environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures to prevent damage or degradation.
Conclusion
Molded gaskets are versatile, durable, and cost-effective sealing solutions that are widely used in various industries. By understanding the different types of molded gaskets, their materials, manufacturing processes, applications, and maintenance requirements, you can choose the right gasket for your specific needs and ensure optimal performance and longevity.
 7
7
7
7 molded gasket. Finishing Finally, the gasket may undergo additional finishing processes, such as cutting, trimming, and buffing, to meet specific requirements.
Applications of Molded Gaskets
Molded gaskets are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and performance. Some of the most common applications include
1. Plumbing Systems Molded gaskets are commonly used in plumbing systems to provide a watertight seal between pipes, fittings, and valves.
2. HVAC Systems In HVAC systems, molded gaskets are used to seal ductwork, air handlers, and other components to prevent air leaks and maintain optimal indoor air quality.
3. Chemical Processing Molded gaskets are ideal for use in chemical processing applications due to their resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures.
4. Food Processing In food processing plants, molded gaskets are used to seal equipment and machinery to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity.
5. Automotive Industry Molded gaskets are used in the automotive industry to seal engine blocks, transmission cases, and other components to prevent leaks and ensure proper operation.
Maintenance of Molded Gaskets
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of molded gaskets. Some tips for maintaining molded gaskets include
1. Regular Inspection Regularly inspect molded gaskets for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Replace any damaged or worn gaskets promptly.
2. Cleaning Clean molded gaskets regularly to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can affect their performance. Use mild cleaning solutions and avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the gasket material.
3. Proper Installation Ensure that molded gaskets are installed correctly and tightened to the recommended torque to ensure a proper seal.
4. Storage Store molded gaskets in a dry, clean environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures to prevent damage or degradation.
Conclusion
Molded gaskets are versatile, durable, and cost-effective sealing solutions that are widely used in various industries. By understanding the different types of molded gaskets, their materials, manufacturing processes, applications, and maintenance requirements, you can choose the right gasket for your specific needs and ensure optimal performance and longevity.
molded gasket. Finishing Finally, the gasket may undergo additional finishing processes, such as cutting, trimming, and buffing, to meet specific requirements.
Applications of Molded Gaskets
Molded gaskets are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and performance. Some of the most common applications include
1. Plumbing Systems Molded gaskets are commonly used in plumbing systems to provide a watertight seal between pipes, fittings, and valves.
2. HVAC Systems In HVAC systems, molded gaskets are used to seal ductwork, air handlers, and other components to prevent air leaks and maintain optimal indoor air quality.
3. Chemical Processing Molded gaskets are ideal for use in chemical processing applications due to their resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures.
4. Food Processing In food processing plants, molded gaskets are used to seal equipment and machinery to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity.
5. Automotive Industry Molded gaskets are used in the automotive industry to seal engine blocks, transmission cases, and other components to prevent leaks and ensure proper operation.
Maintenance of Molded Gaskets
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of molded gaskets. Some tips for maintaining molded gaskets include
1. Regular Inspection Regularly inspect molded gaskets for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Replace any damaged or worn gaskets promptly.
2. Cleaning Clean molded gaskets regularly to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can affect their performance. Use mild cleaning solutions and avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the gasket material.
3. Proper Installation Ensure that molded gaskets are installed correctly and tightened to the recommended torque to ensure a proper seal.
4. Storage Store molded gaskets in a dry, clean environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures to prevent damage or degradation.
Conclusion
Molded gaskets are versatile, durable, and cost-effective sealing solutions that are widely used in various industries. By understanding the different types of molded gaskets, their materials, manufacturing processes, applications, and maintenance requirements, you can choose the right gasket for your specific needs and ensure optimal performance and longevity. Next: